Spinal canal stenosis/ Targeted Conditions
What is spinal stenosis?
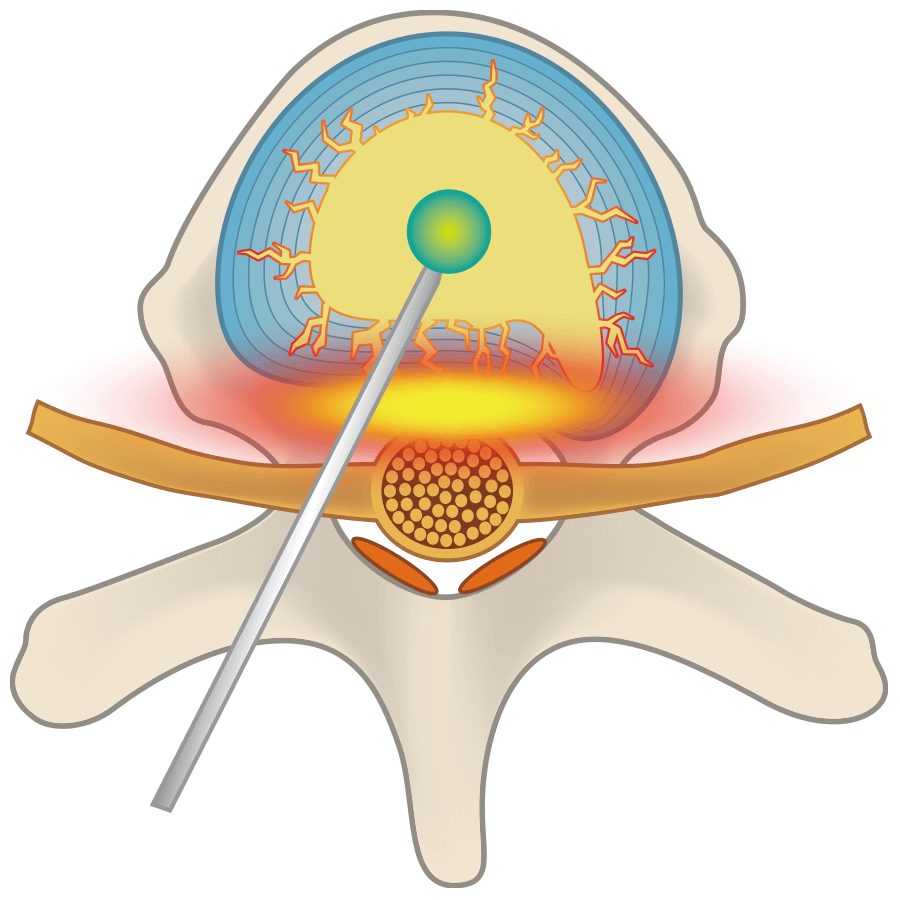
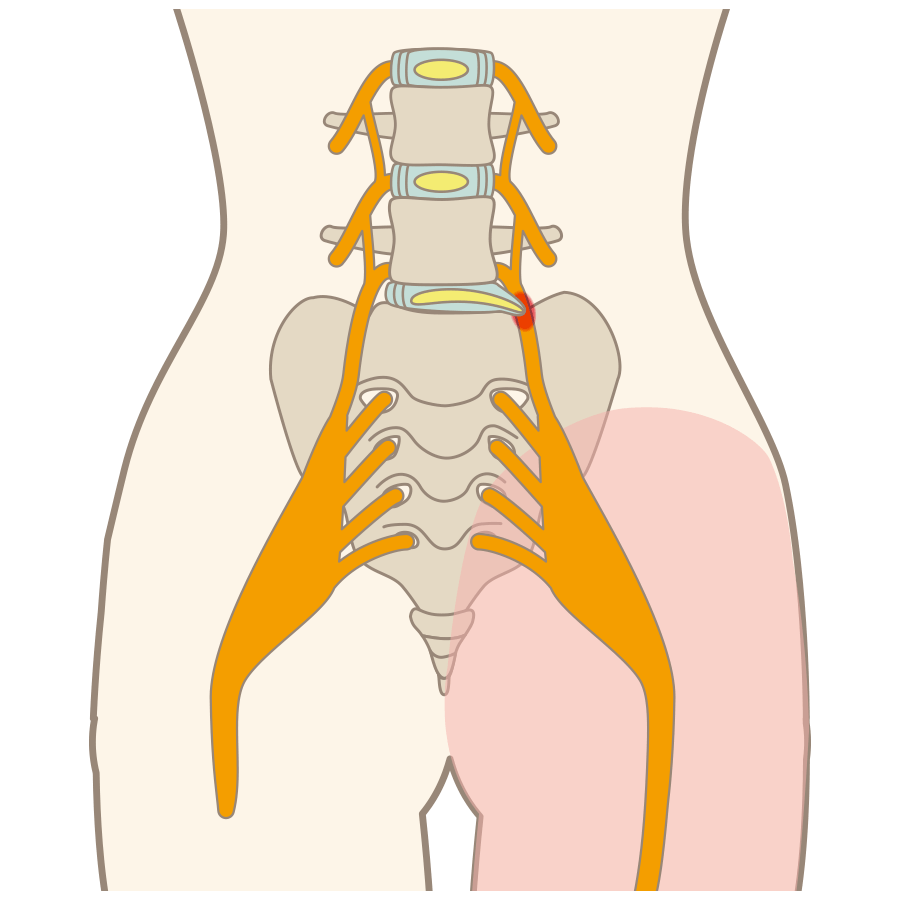
“Spinal stenosis” refers to a condition in which the path for nerves within the spine has narrowed. That path for nerves is called the “spinal canal.” Broadly speaking, the spine is made of three things, as in the illustration: [1] bone, [2] intervertebral discs, and [3] nerves.
Normal intervertebral disc
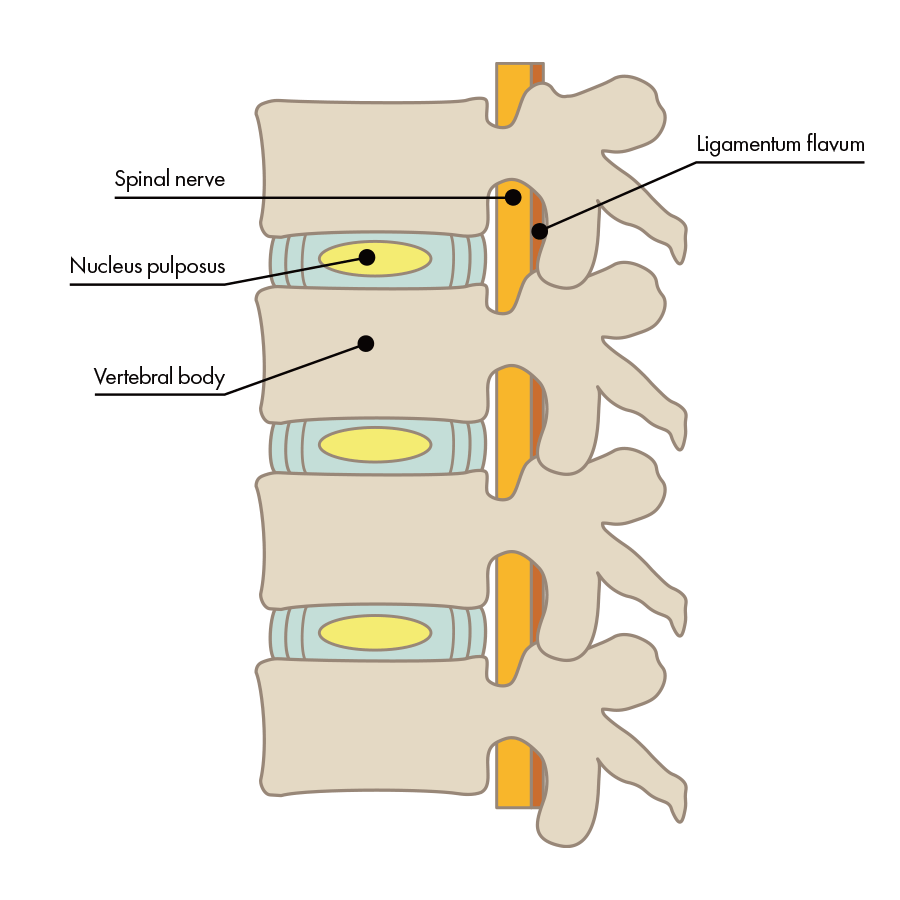
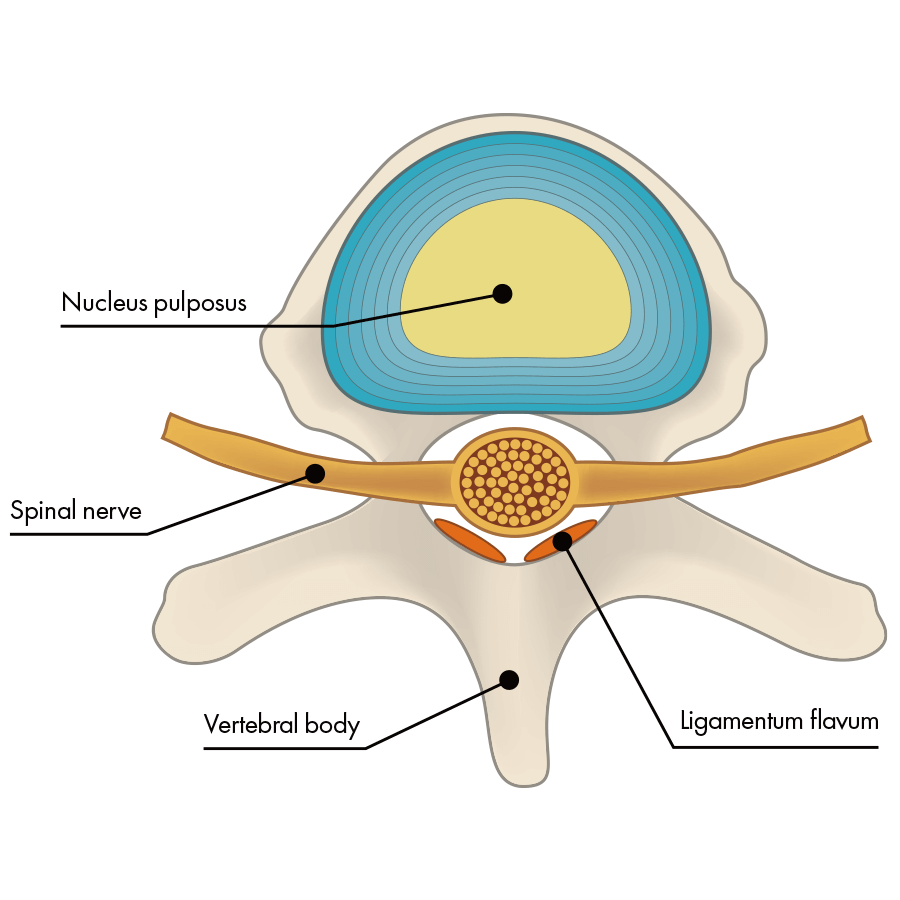
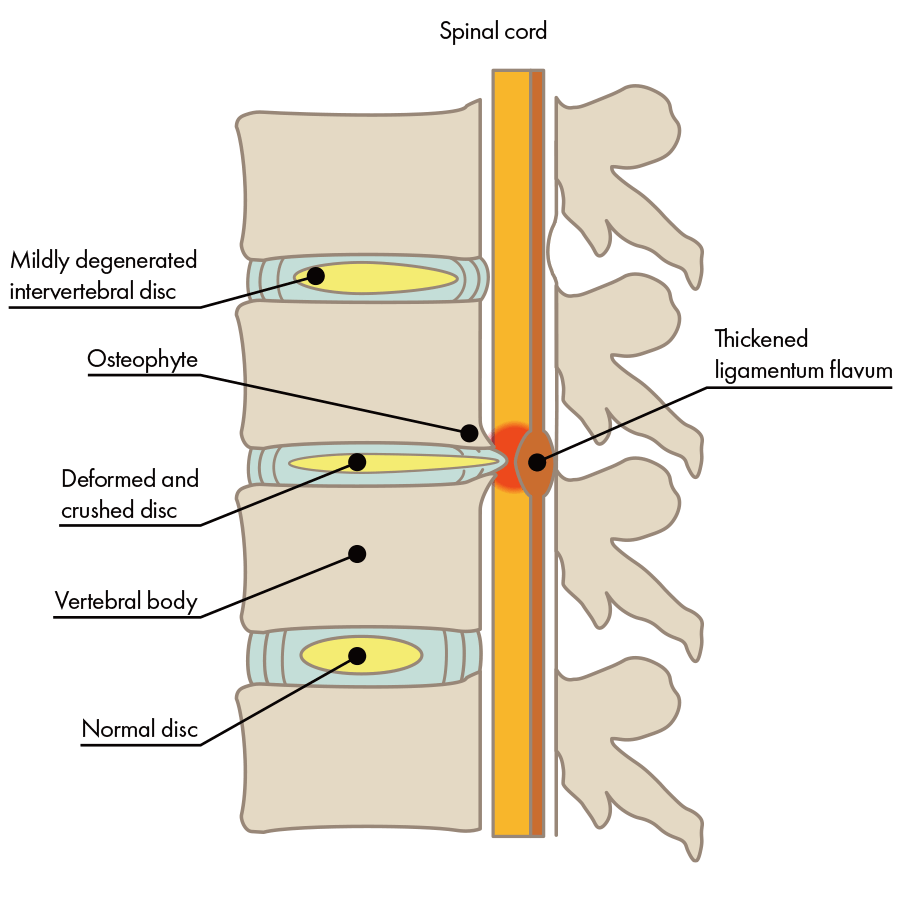
The condition in which the spinal canal in the lower back is narrowed is called "lumbar spinal stenosis." When lumbar spinal canal stenosis is caused by instability of the lumbar spine, physical movement often causes pain.
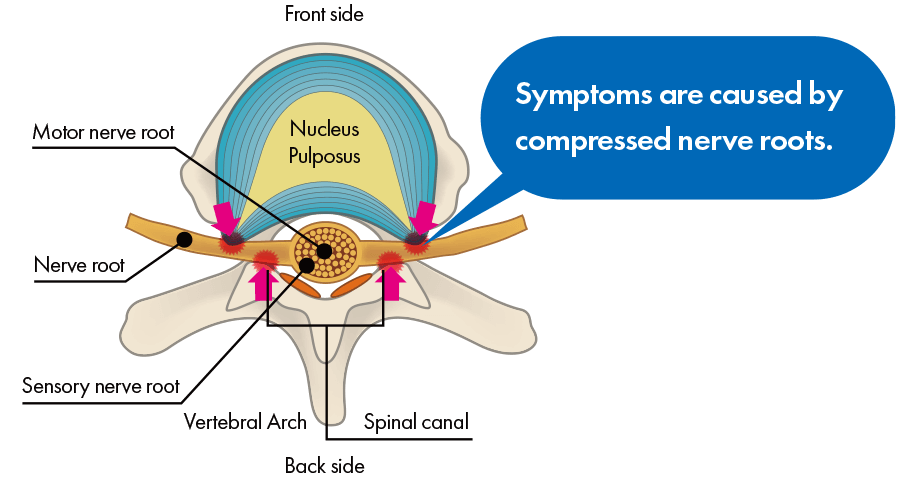
Nerve Root Type
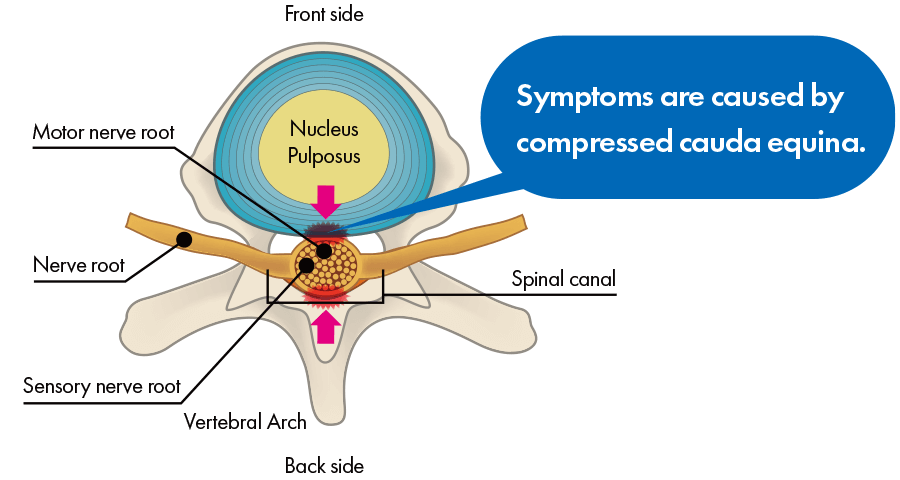
Cauda Equina Type
Mixed Type
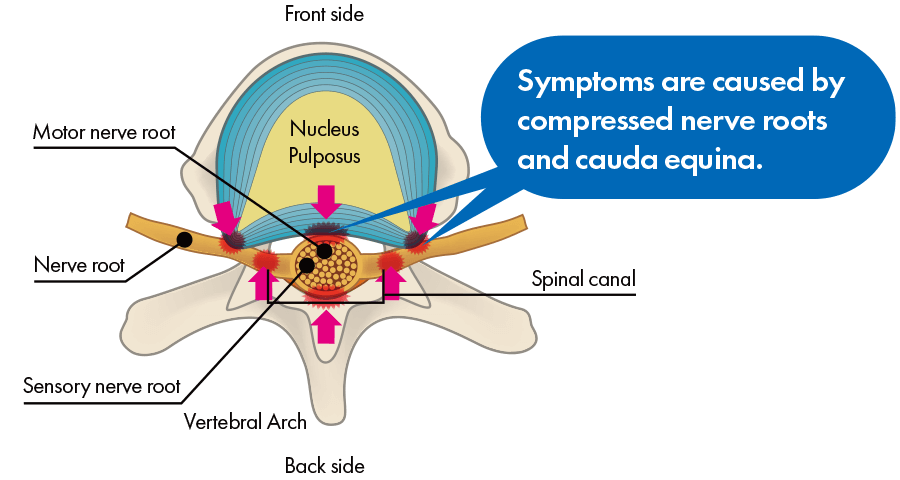
When you get spinal stenosis, numbness or pain appears in your low back and legs. For example, it is similar to how your legs become numb if you kneel and sit back on your heels for a long time and pressure is placed on the sciatic nerves on the backs of your thighs, and if the pressure continues without stopping, pain appears in your legs. Furthermore, because pressure on the nerves is not strong in symptoms’ early stages, even if you do not feel numbness or pain in most situations, pressure becomes strong when you exercise, and pain and numbness may appear with intensity. That type of phenomenon in which numbness and pain occur when you exercise is called “intermittent claudication.” It is also called “intermittent claudication” when your calf muscles hurt and you cannot continue walking.
What are the symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis?
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis can cause numbness and pain in the lower back and legs. Just like, keeping a kneeling position for a long time having the sciatic nerves on the back side of the thighs compressed makes feet become numb, and eventually start to hurt. In the early stages of the disease, when pressure on the nerves has not risen to the point to cause numbness and pain, certain exercises like walking may add to it and trigger the symptoms in the muscles of the calves or other parts of the body making it impossible to continue. The phenomenon of numbness and pain during exercise is called intermittent claudication.
What are the causes of spinal stenosis?
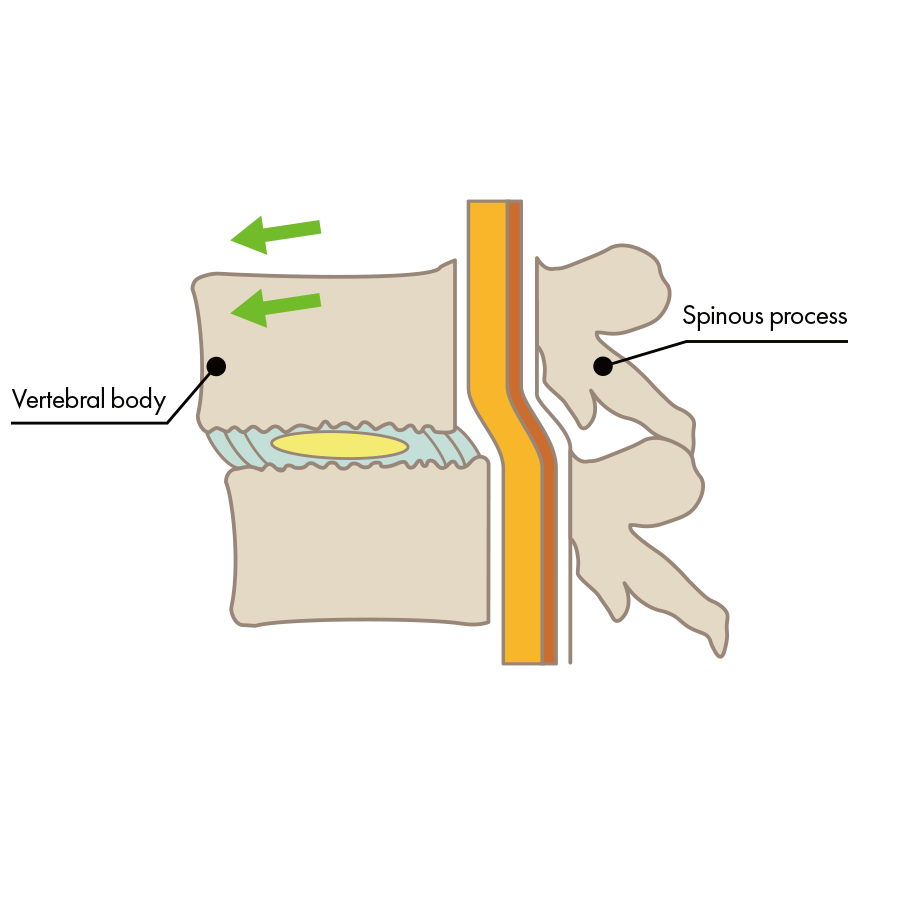
Difficulty walking, pain or numbness in the thighs, pain while walking and then needing to rest to walk again, pain in the lower back when stretching the back, pain when standing, pain when rising up and out of bed, are some of the walking impediments that are attributed to spinal stenosis, and difficulty to walk due to spinal stenosis, and the inability to walk without resting in the middle of a walk are some of the many symptoms that interfere with daily life that are characterized as originating in the nerves. There are several possible causes for these symptoms which put pressure on the nerves, which have only been identified in recent years.
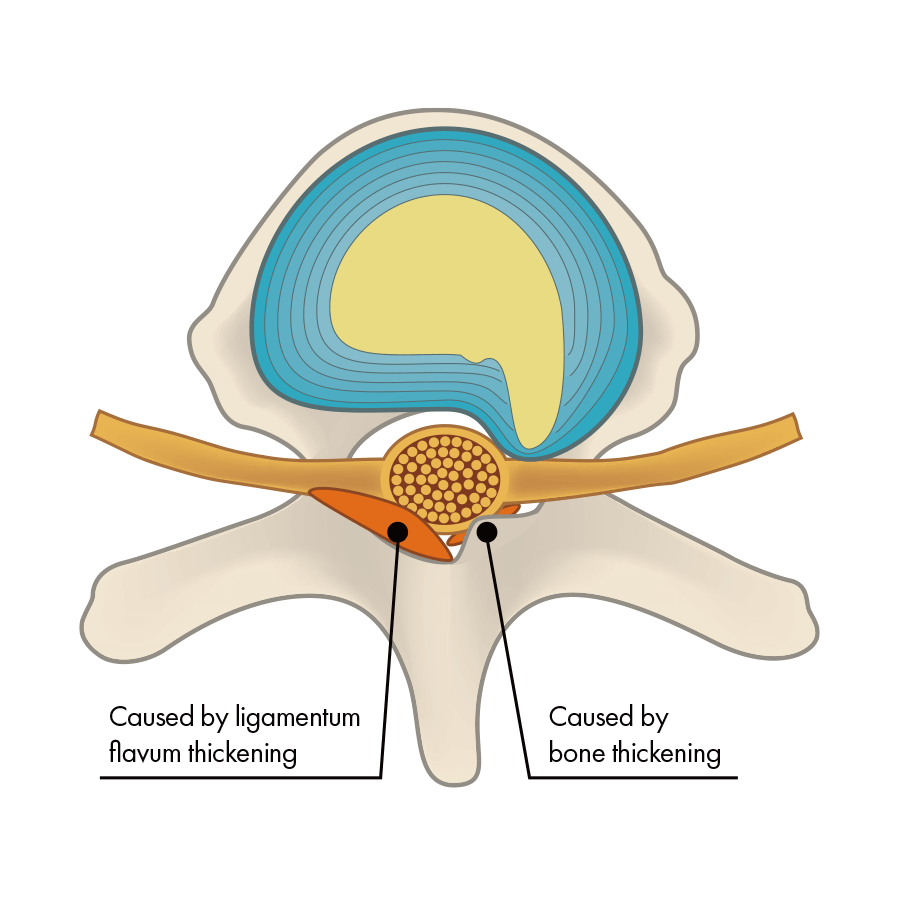
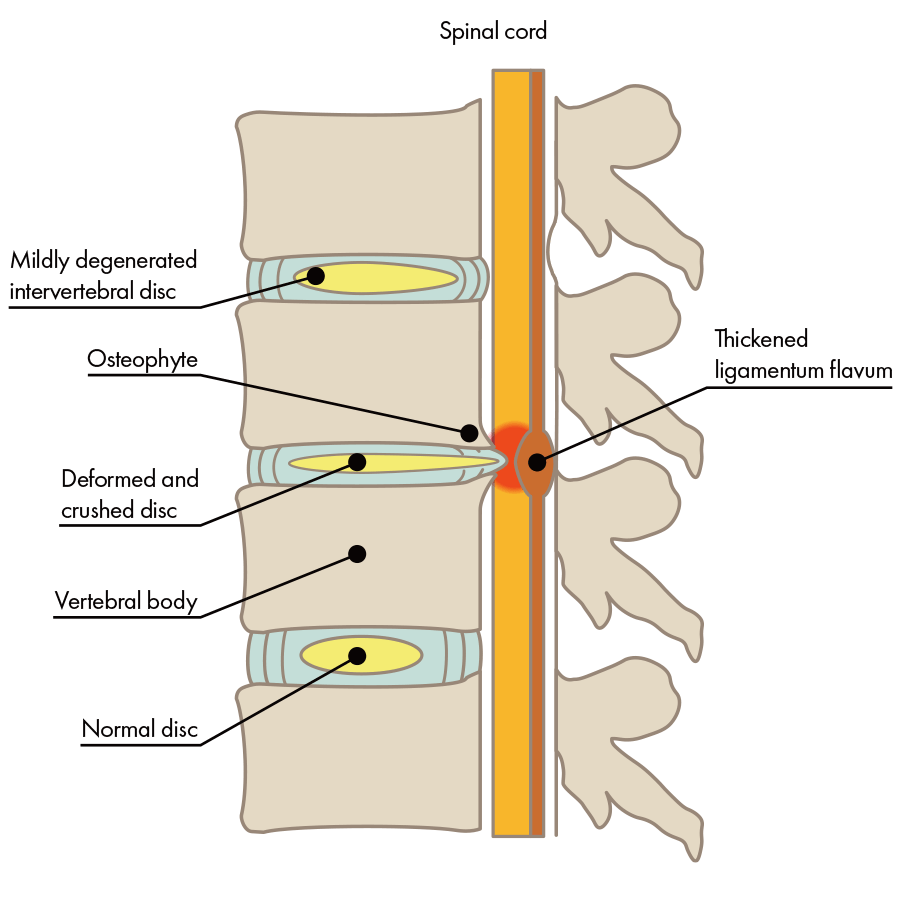
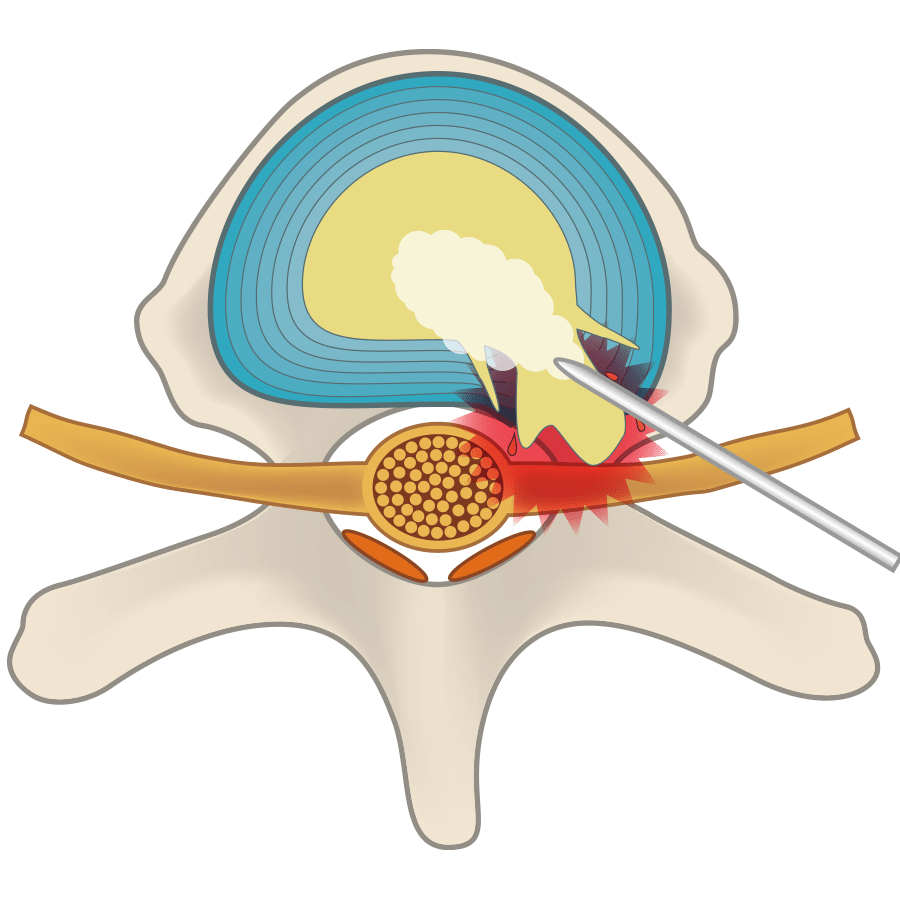
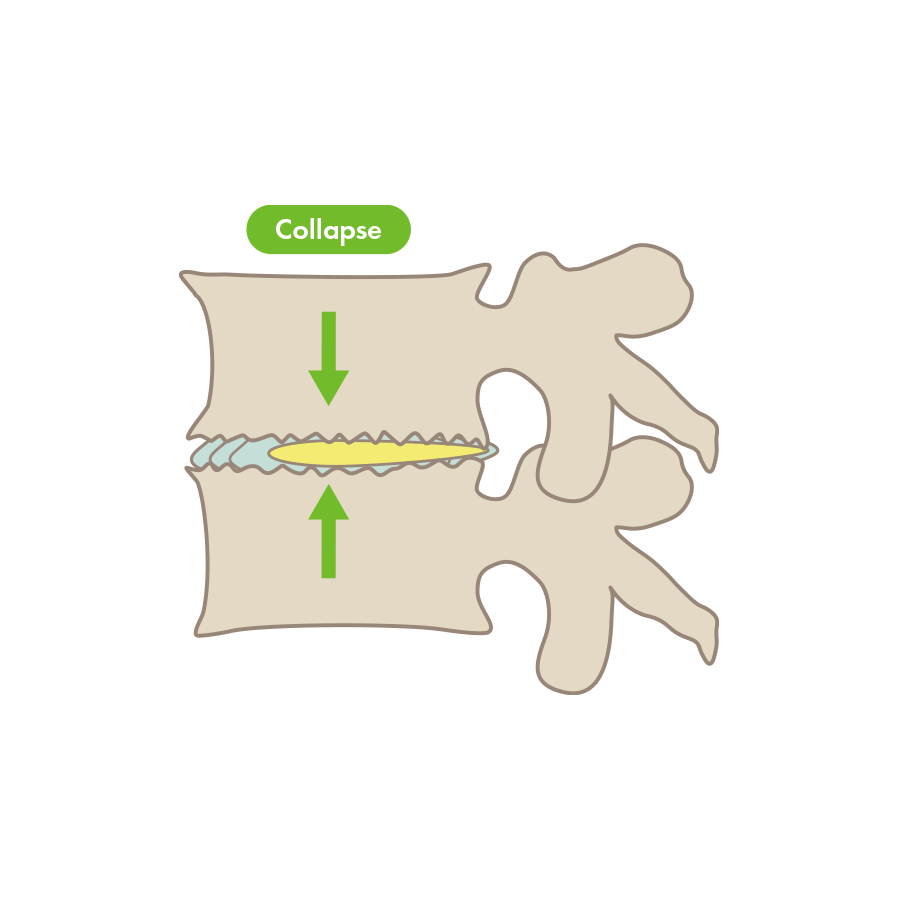
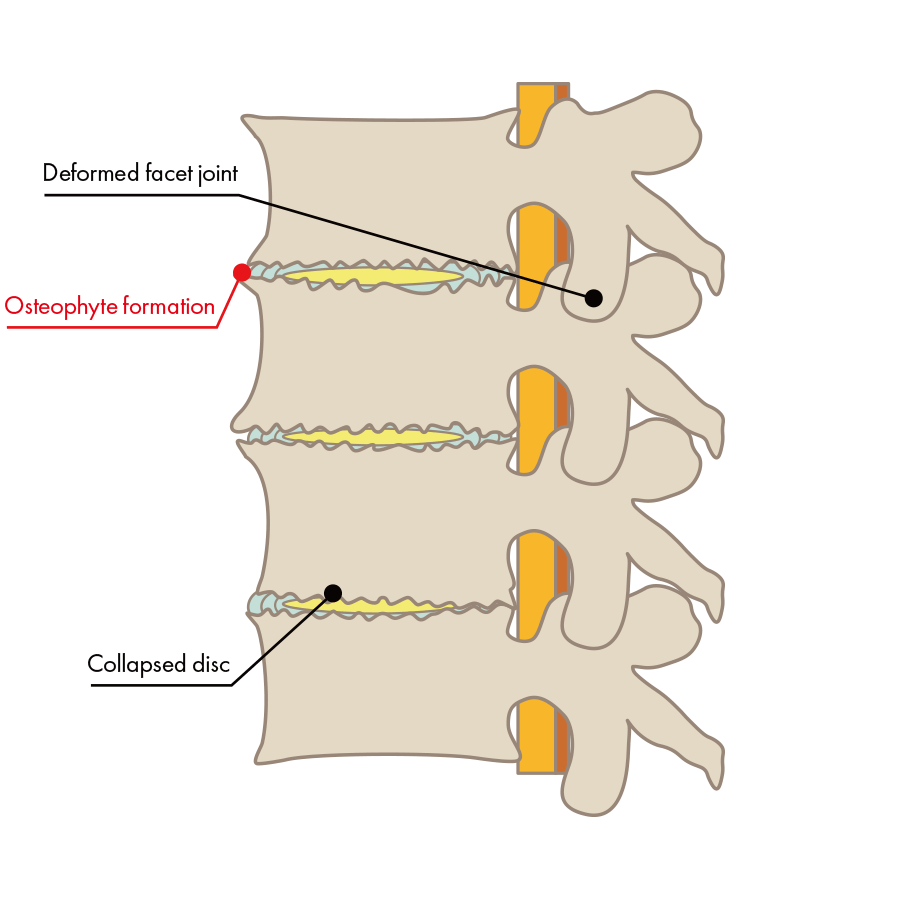
The intervertebral disc has collapsed, the bone is deformed, and pressure has been placed on the nerve.
Surgical treatment for lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Lumbar Laminectomy
This is a surgical procedure to widen the narrowed lumbar spinal canal caused by stenosis. There are two types of laminectomy: wide laminectomy, in which the vertebral arch is extensively resected, and partial laminectomy, in which only the part of the vertebral arch that stands in way of passing the endoscope is removed. When wide lumbar laminectomy is performed, a 4 cm skin incision on the back is made and after the the muscles are detached from the bone, the lumbar vertebral arch is cut out, and the thickened part of the yellow ligament that causes the stenosis is removed. During partial laminectomy, after making an incision of 1.5 cm to 2 cm in the skin, a 1.2 ~1.8 cm wide surgical instrument with a camera attached to its tip is inserted into the spine. The whole process of removing a portion of the vertebral arch, ligaments etc. to decompress the nerve is monitored on an external screen.
Advantages of Lumbar Laminectomy
When partial lumbar laminectomy is used, due to the narrow incision, the wound is small and the patient can leave the hospital in about a week.
Disadvantages of Lumbar Laminectomy
In the case of partial lumbar discectomy, the incision is narrower, but the field of vision is also limited, so the procedure cannot be performed if there are multiple areas of stenosis or if the vertebrae are not stable. In the case of wide laminectomy, the incision is wider and the risk of infection and complications is higher. Furthermore, revision surgery may not be possible after wide laminectomy has been done.
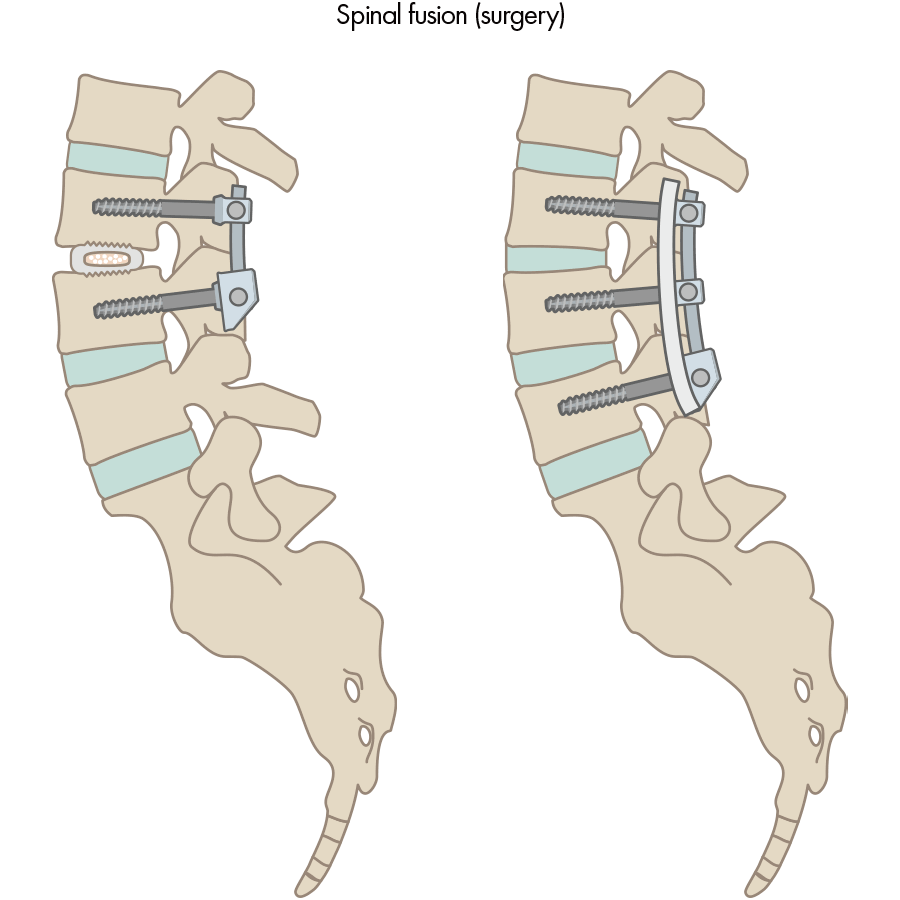
Spinal Fusion Surgery
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that uses medical devices such as plates, screws, rods and spacers to fix a part of the spine that is suffering from spinal canal stenosis. General anesthesia is performed and an incision is made in the skin of the back. A part of the spine called the vertebral arch and the facet joints are cut out, and the intervertebral disc and ligamentum flavum are removed. A spacer is inserted in place of the disc, and a plate is set and fixed with rods and screws.
Advantages of Spinal Fusion Surgery
This surgical procedure is used to treat a wide range of lumbar spine diseases including spinal canal stenosis and disc herniation etc. Since it immobilizes the spine, it can be effective in cases where the lumbar spine is unstable.
Disadvantages of Spinal Fusion Surgery
Postoperative rehabilitation is required, which makes a hospital stay of approximately one month inevitable. The risk of infection and complications is higher in spinal fusion surgery than in minimally invasive surgery due to the wider incision and longer operation time, and patients may experience discomfort and pain due to postoperative rehabilitation and immobilization. Similar to the MEL method, it is a surgical operation that makes conditions difficult to re-operate.
If there is no improvement at all with conservative treatment, or if the pain and numbness are so strong that the patient cannot walk or has trouble urinating, surgical operation may be an option. At our clinic, we offer the minimally invasive Discseel® Procedure as an alternative treatment to surgical operations like laminectomy, spinal fusion surgery etc.
Conservative treatment for lumbar spinal canal stenosis
Medication Treatment
Medical institutions usually prescribe medicine for external use such as compresses and ointments, anti-inflammatory analgesics to suppress inflammation, and muscle relaxants to relieve back pain by relieving muscle tension when diagnosed with back pain. If the cause of low back pain is nerves, vitamins may be taken for them to recover.
Advantages of Medication Treatment
Temporarily relieves pain and numbness. It can be prescribed according to the intensity of the symptoms.
Disadvantages of Medication Treatment
Side effects are strong and may not be suitable for some patients, so it is necessary consult with a doctor while taking it. Continued medication may gradually lose its effect.
Thermotherapy
The purpose of thermotherapy is to warm the lower back and improve poor blood circulation.
Advantages Thermotherapy
By improving blood circulation, metabolism becomes more active, and fatigue and chemical substances are no longer retained, which is expected to relieve back pain and recover from fatigue. Hospitals and osteopathic clinics often use hot packs and electric massage to manage symptoms caused by lumbar spinal canal stenosis.
Disadvantages of Thermotherapy
Warming the lower back for acute back pain may aggravate the inflammation instead of letting it calm down. As it is not a fundamental treatment, the pain may reappear after a while.
Physical Therapy
When back pain appears as a result of lumbar spinal stenosis a rest may be taken, but longer periods of rest may prolong the symptoms.
Advantages of Physiotherapy
Physical exercises and stretching is important because it may help improvement. When training the abdominal and back muscles, have to be careful not to strain the back, because putting excessive pressure on the nerves and muscles can worsen the inflammation and make symptoms reappear.
Disadvantages of Physiotherapy
It is used to deal with a wide range of spinal diseases such as lumbar spinal canal stenosis and disc herniation, but training the abdominal back muscles is not everything, and incorrect methods or straining the muscles may worsen back pain. Please make sure you seek the advice from a doctor.
Conservative treatment is often the first choice for spinal canal stenosis, because it offers a variety of ways to improve the patient's condition only with medication and physical therapy.
How Is Our Clinic’s Treatment Effective for Spinal Stenosis?
First, since surgery for spinal stenosis exists, we would like simply to do a comparison. Surgery began typically to be performed in the 1960s, but bone was removed, immobilizing the area was sometimes necessary, the risks of surgery were high, and it was not a treatment of the root cause, so the high recurrence rate of 30-46% (within 2 years) was a problem. Now people have figured out how to use endoscopes and make the scar small, but by the same principle, surgery does not treat the root cause, so the risks and recurrence rate remain high.
Intervertebral disc treatment taking into consideration the problems with surgery explained above began in the 1980s. At present, The Discseel® Procedure has also begun. The principle of The Discseel® Procedure is that it is a treatment that, by improving intervertebral disc function, can improve the burden on the bones, at the same time eliminating pressure on the nerves. The Discseel® Procedure’s distinguishing features are that the risks are extremely low because it just repairs intervertebral discs, and the recurrence rate is low because it treats the root cause of spinal stenosis.
Since this treatment has a low-risk and low recurrence rate, the toll on the body is minimal. In addition, since the needle is very thin, the wound left is small and usually closes in a week, with no scar apparent. At our hospital, the consultations are conducted in the morning and the treatments are performed in the afternoon, which makes it easier for patients who live far away or overseas to undergo the treatment. The procedure is performed as an ambulatory treatment. We can also conduct remote image diagnosis in advance to determine if The Discseel® Procedure is applicable.
Treatment Overview
-
The Discseel
Discseel® Procedure

Discseel® Procedure was developed by an American surgeon by the name of Dr. Kevin Pauza, after caring for hundreds of patients who were made worse following their spine surgery. The treatment aims to seal tears in herniated vertebral discs and help them regenerate and recover their, allowing permanent relief of back pain. Dr. Pauza holds a series of 16 patents for a device and Discseel® biologic that support the treatment. Dr.Nonaka has been licensed to perform the Discseel® Procedure in 2018, and more than 2,880 patient have undergone the treatment in our clinic since then. At present, approximately 20 doctors, including physicians from Harvard and Boston Universities are using the Discseel® Procedure to treat their patients in the USA. Dr. Nonaka is the first physician trained to perform the Discseel® Procedure in Japan.
-
The PODT Method
(Ozone)Percutaneous Ozone Disc
Treatment
PODT is a method that improves low back pain due to discitis or herniated discs or nerve pain due to spinal stenosis by using a 0.8 mm puncture needle to inject ozone into the intervertebral disc’s nucleus pulposus. We cannot say that the particulars of ozone’s anti-inflammatory effect have been elucidated, but it is thought that, by stimulating the inside of the body, ozone treatment intentionally produces a strong immune response and puts an end in a short time to any inflammation that has occurred. The ozone itself is only injected inside the intervertebral disc, but the treatable conditions are not confined to herniated discs: the treatment is also effective for spinal stenosis or vertebral canal stenosis. The reason is believed to be that the ozone injected into the intervertebral disc passes through the damaged disc and permeates surrounding tissue. With the patient under local anesthesia, and while using an X-ray fluoroscope, we safely place a 0.8 mm puncture needle into the intervertebral disc. After that, we inject ozone in proportion to the state of the damage. We finish by checking with the X-ray fluoroscope whether ozone has permeated into and outside of the intervertebral disc.
Spinal canal stenosis: FAQ
-
- Q
-
Which symptoms will prompt the necessity of a surgery for spinal stenosis?
- A
-
Surgery may be an option if the patient has trouble with daily activities, such as difficulty walking or urinating, or if the pain or numbness is so severe that it cannot be tolerated.
-
- Q
-
Do I have to undergo surgery if I have been diagnosed with spinal canal stenosis ? Will it heal spontaneously if left unoperated?
- A
-
It will be difficult to recover naturally. Since surgery is one of the ways to treat spinal canal stenosis, it is important to listen to your doctor's opinion, discuss and choose the best treatment method.
-
- Q
-
Will I lose my ability to walk in the future if I fail to have spinal stenosis surgery?
- A
-
It all depends on the patient's symptoms and condition, but if the symptoms are severe, the patient may eventually lose the ability to walk.
-
- Q
-
Is disc herniation a dangerous disease?
- A
-
Many patients may experience severe symptoms, and they may not be able to sit or walk. The most important thing to do first is to see a doctor and find the most appropriate treatment.
-
- Q
-
What other treatments are available for spinal stenosis?
- A
-
The other options are all surgical procedures: Spinal fusion or endoscopic surgery to stabilize your back by shaving the bones and discs before securing the bones in place.
-
- Q
-
Can't conservative treatment cure spinal stenosis?
- A
-
No, it cannot, because the cure can never be complete. Treatments intended to relieve pain and numbness cannot be considered as root treatments. The Discseel® Procedure is the only treatment that can repair the discs that are causing the pain; therefore, it is the only treatment that can alleviate the pain at root level.
-
- Q
-
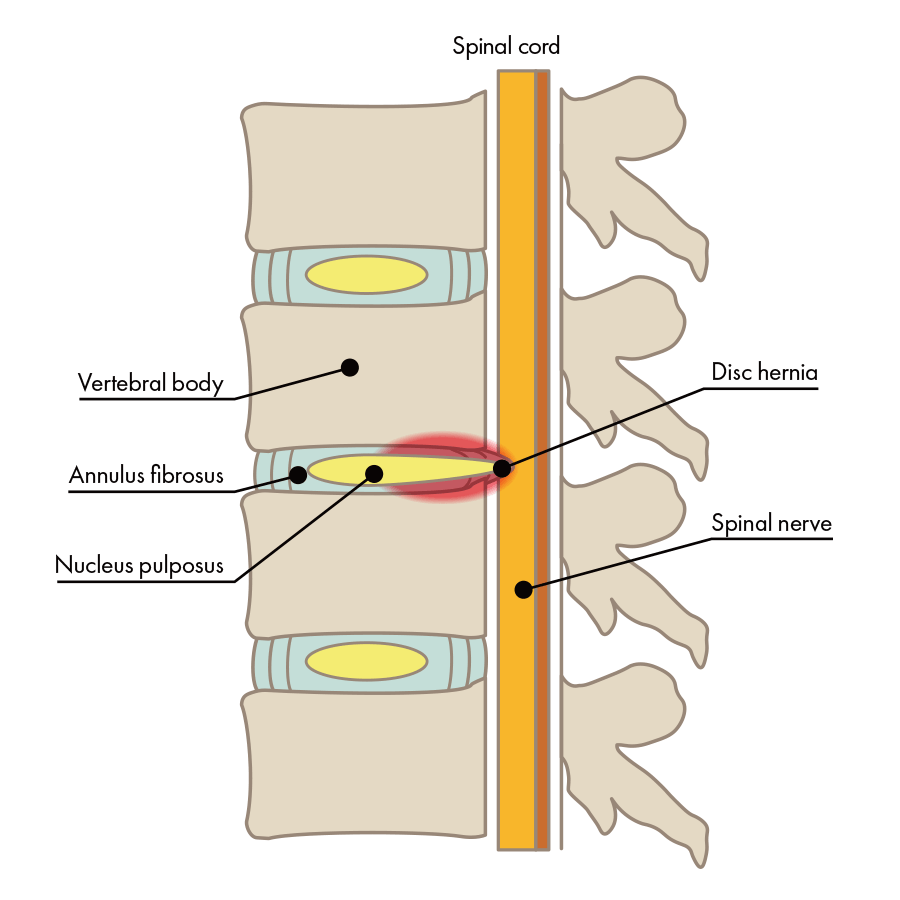
What is the difference between spinal canal stenosis and disc herniation?
- A
-
The difference between disc herniation and spinal canal stenosis is that disc herniation refers to a disc pressing on a nerve, while spinal canal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the spinal canal. If the disc herniation progresses to the point where it protrudes into the spinal canal, the pathway for the nerves in the spine, and narrows its space, the result is spinal canal stenosis.
-
- Q
-
I was diagnosed with spinal stenosis and underwent spinal fusion, but the pain has not subsided. Can the Discseel® Procedure help me?
- A
-
Once we have diagnosed your condition, we will be able to treat you even if you have already undergone a spinal fusion surgery in the past. Please feel free to contact us for a consultation.
-
- Q
-
I have been diagnosed with scoliosis, is there any treatment other than surgery?
- A
-
In addition to surgery, there is a variety of other ways to treat spinal canal stenosis such as medication treatment, thermotherapy, and physical therapy etc.
-
- Q
-
What is the difference between lumbar spondylolisthesis and lumbar spinal canal stenosis?
- A
-
Lumbar spondylolisthesis refers to a deformed disc that fails to maintain its shape and slips forward, compressing the nerve behind it and causing pain. Spinal canal stenosis is an inflammation around the nerve due to deformity and instability of the spine itself, caused by pressure from the back and side of the nerve in the spinal canal, which.
Targeted Conditions
-
Disc Herniation

-
Spinal Canal Stenosis

-
Sciatica

-
Spondylolisthesis

-
Disc Degeneration

-
Lumbar Spondylosis

- HOME/
- Targeted Conditions/
- Spinal canal stenosis