Disc Herniation/ Targeted Conditions
What is disc herniation?
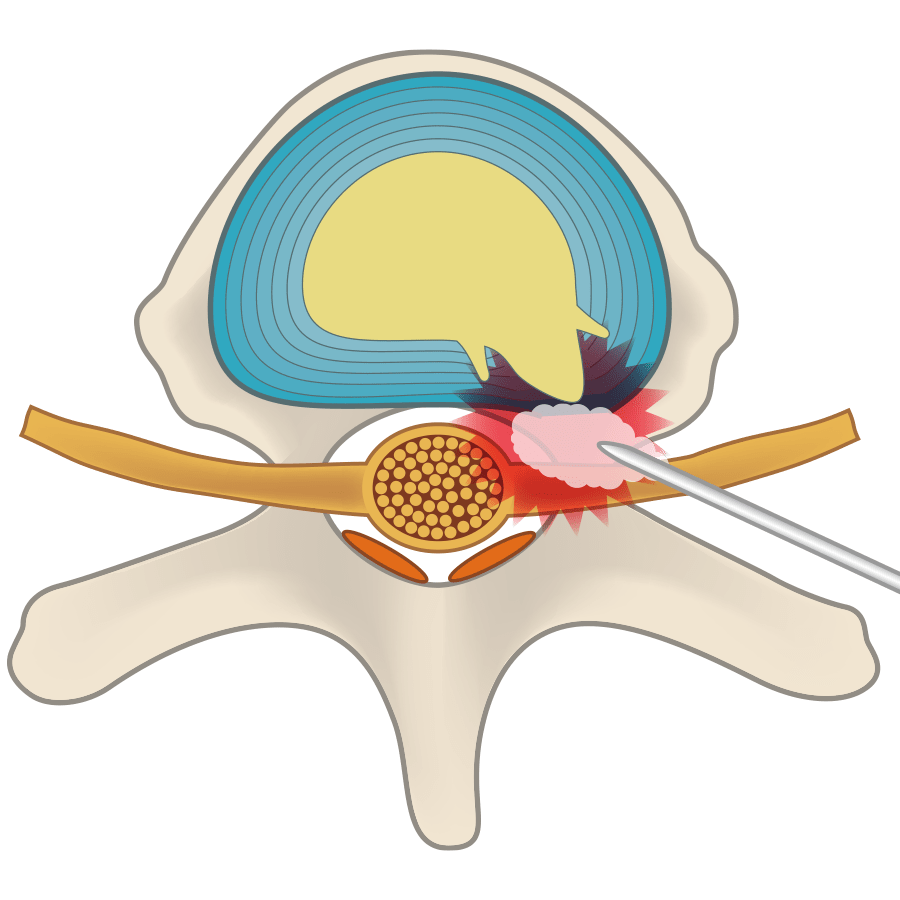
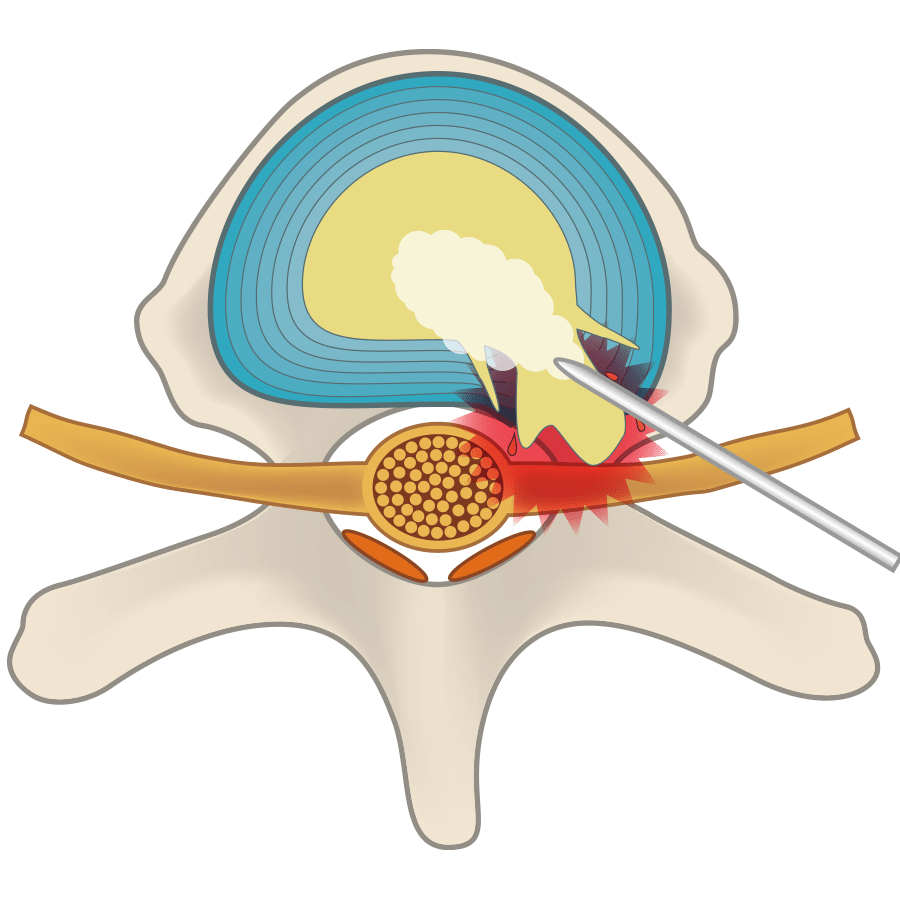
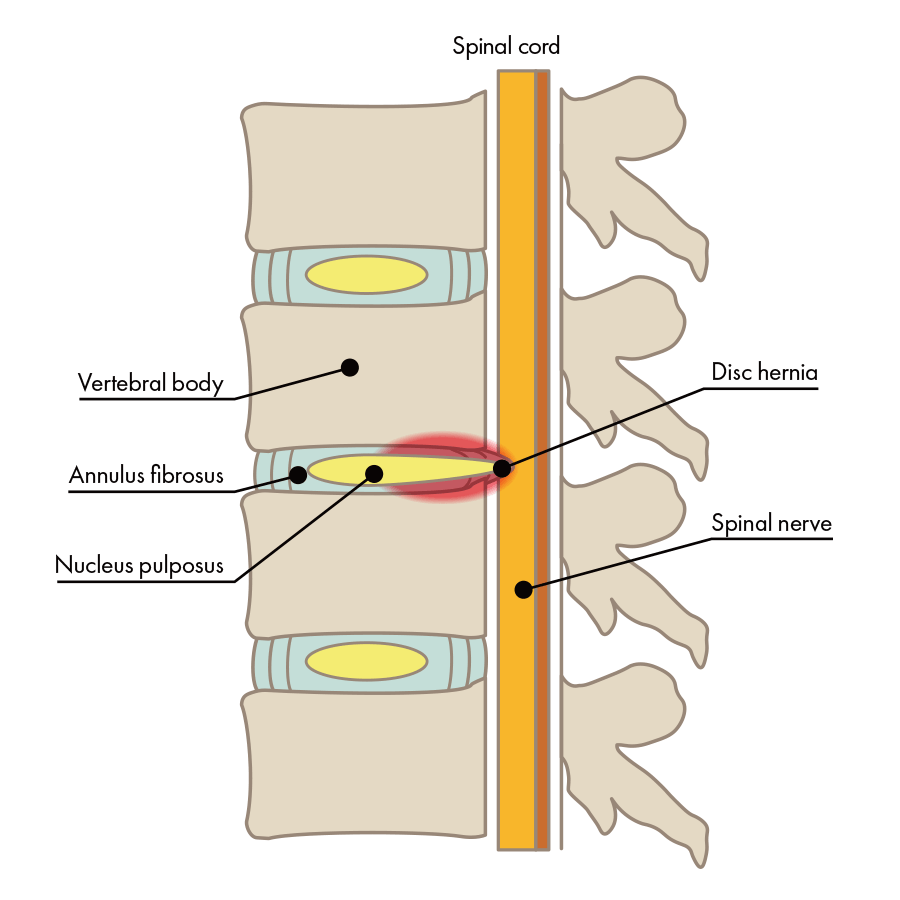
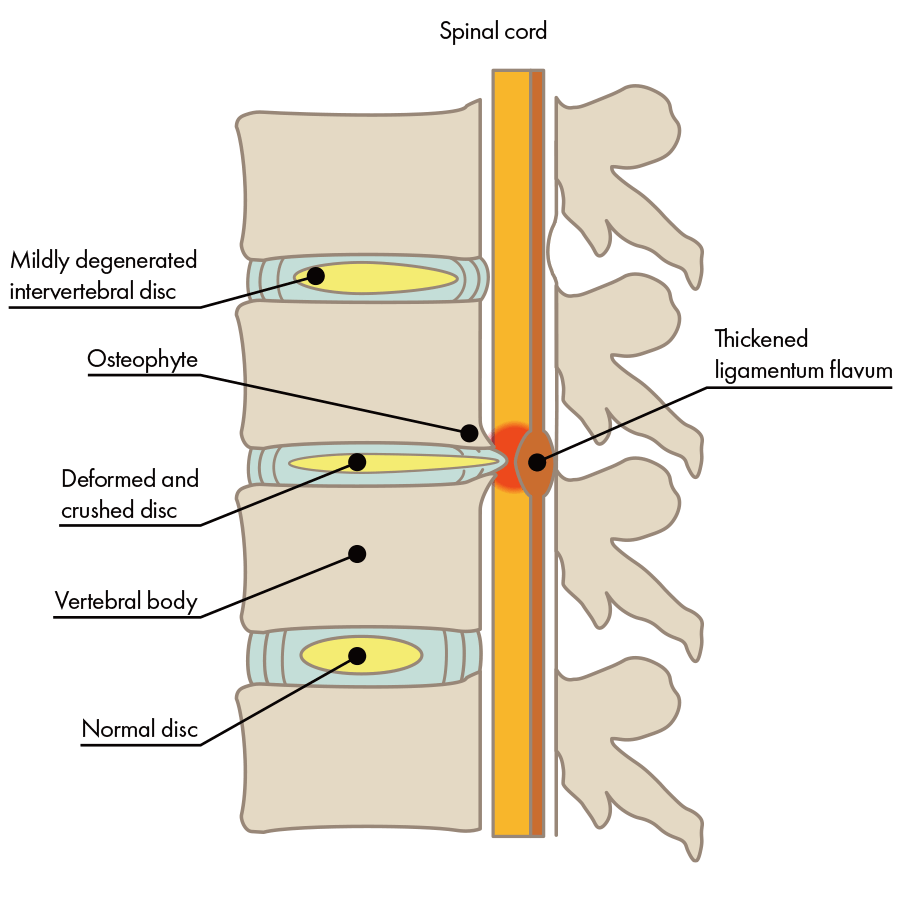
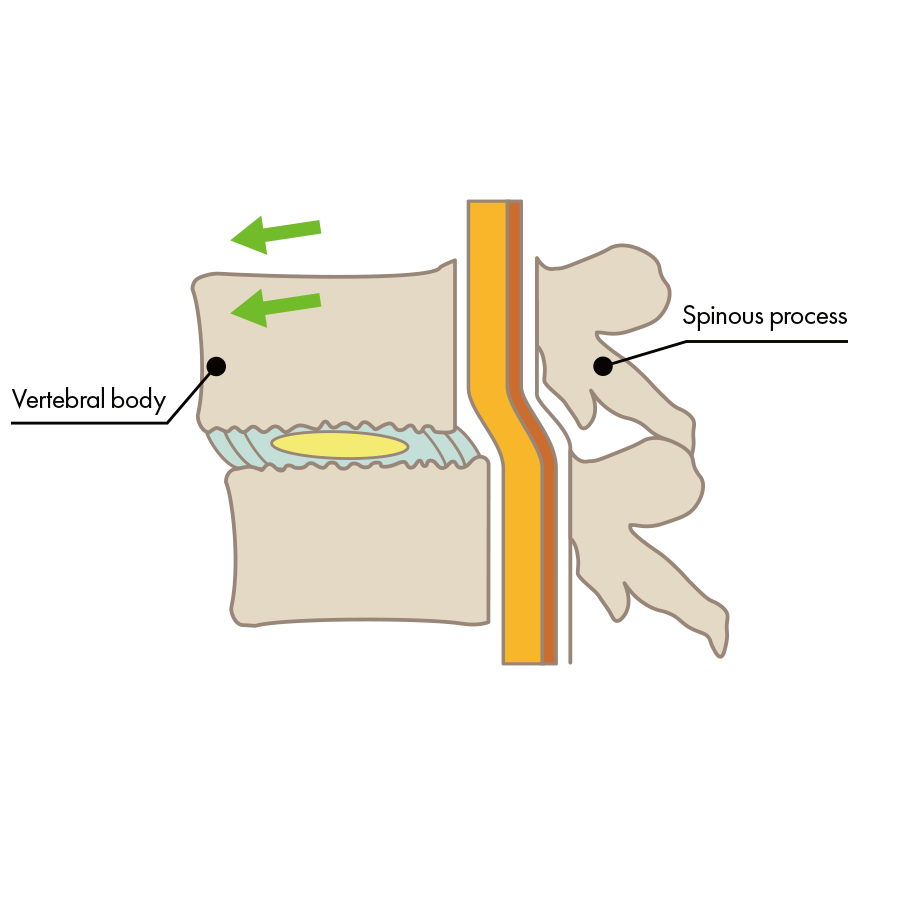
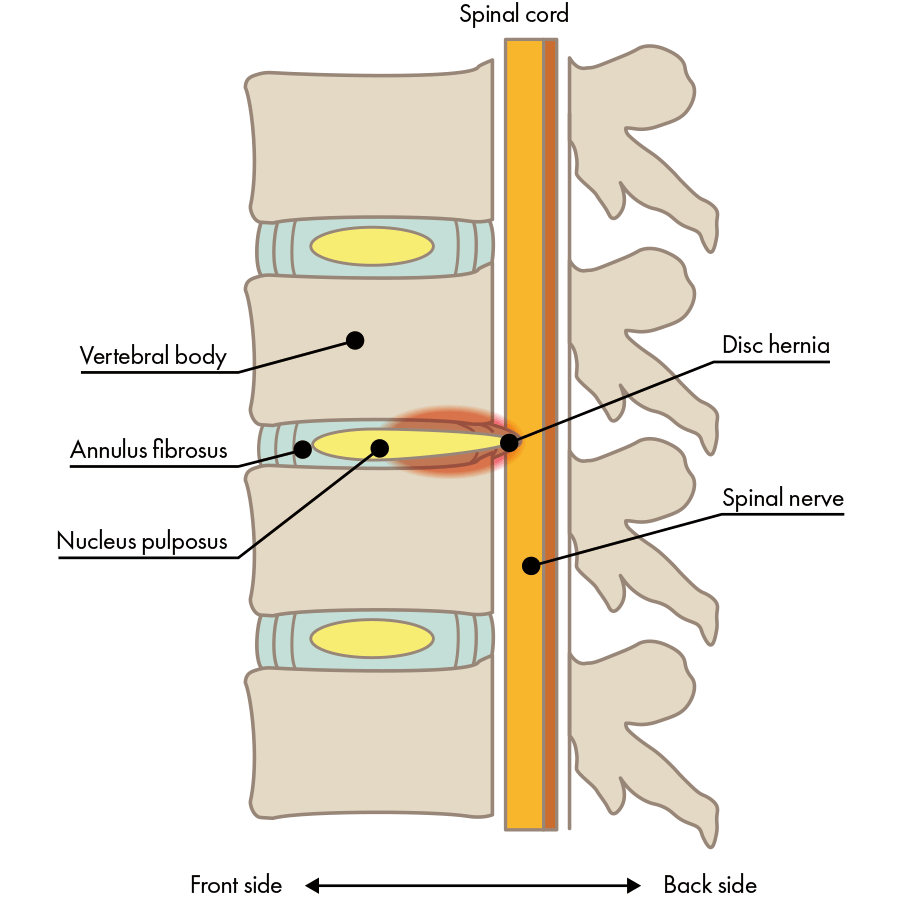
Explained simply: between vertebrae are intervertebral discs, and in the center of the intervertebral discs there’s the gelatinous nucleus pulposus; surrounding the nucleus pulposus is a fibrous ring that contains an abundance of collagen. Intervertebral discs are made up of both of these types of tissue: nucleus pulposus and the fibrous ring. Disc herniation is the state of a vertebral disc in which the nucleus pulposus has escaped through cracks in the fibrous ring.
There are roughly 2 types of disk herniation.
Contained Herniation
(Disc Protrusion)
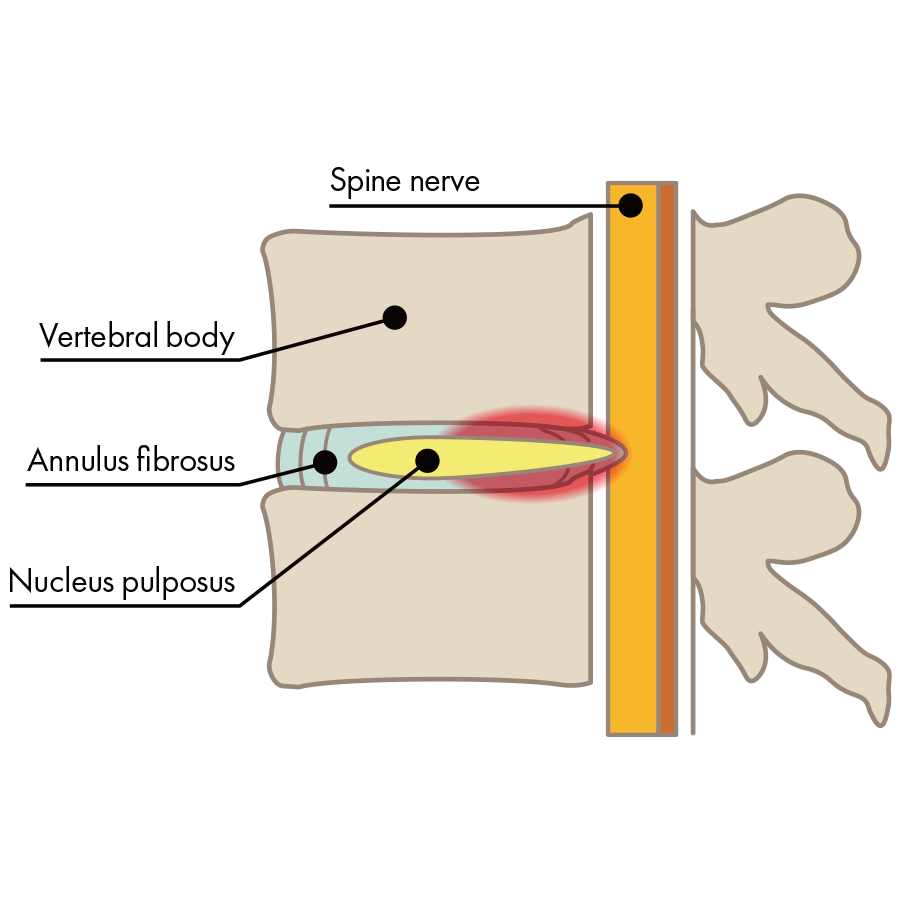
In this type, there are few cracks in the fibrous ring, and nucleus pulposus does not escape. However, nucleus pulposus does transfer backwards and place pressure on part of the nerve.
Non-Contained Herniation
(Disc Extrusion)
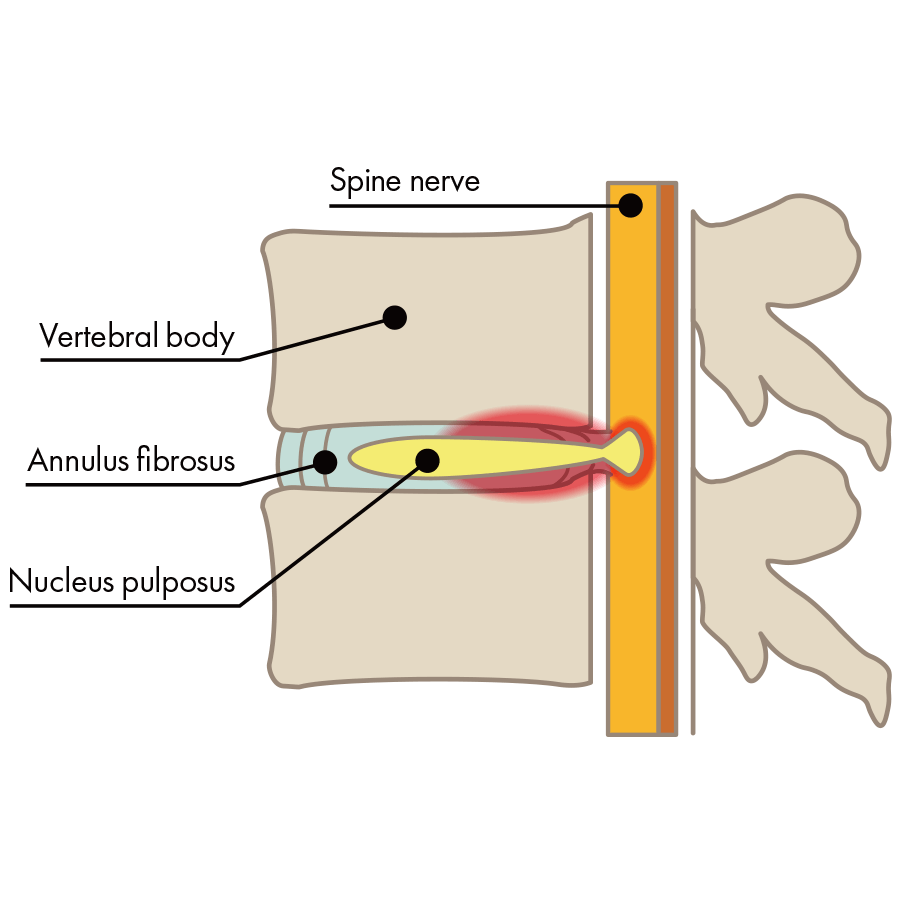
In this type, cracks appear in the fibrous ring due to intervertebral disc damage, and nucleus pulposus breaks through the fibrous ring and places pressure directly on the nerve.
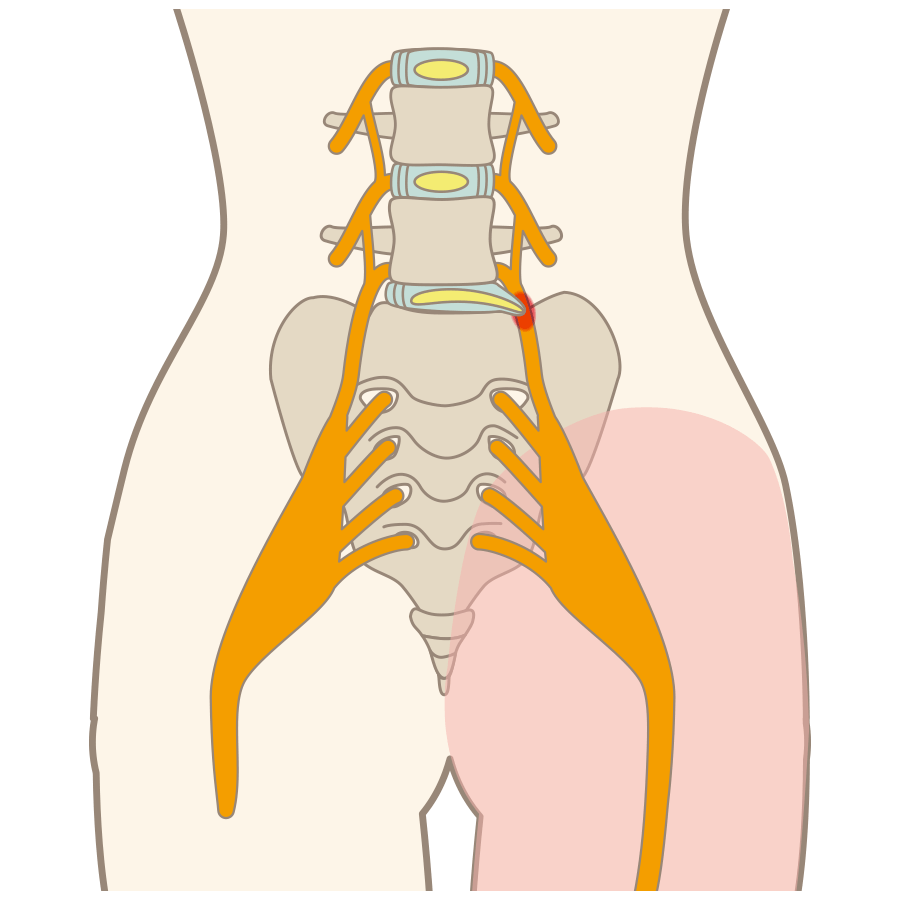
Symptoms associated with lumbar disc herniation
Herniation of a disc in the lower back is called a lumbar disc herniation, and the main symptoms are pain, numbness and weakness in the buttocks and legs. There are two types of lumbar disc herniation: acute and chronic. The acute type may occur when a person lifts a heavy load or just sneezes, etc. Acute back pain is also known as "lumbar sprain". The symptoms of the acute lower back pain usually diminish gradually within a week to a month. However, if the discs are damaged due to the recurring condition, the nucleus pulposus is pushed out from the discs and presses on the nerves, causing chronic pain.
What causes disc herniation?
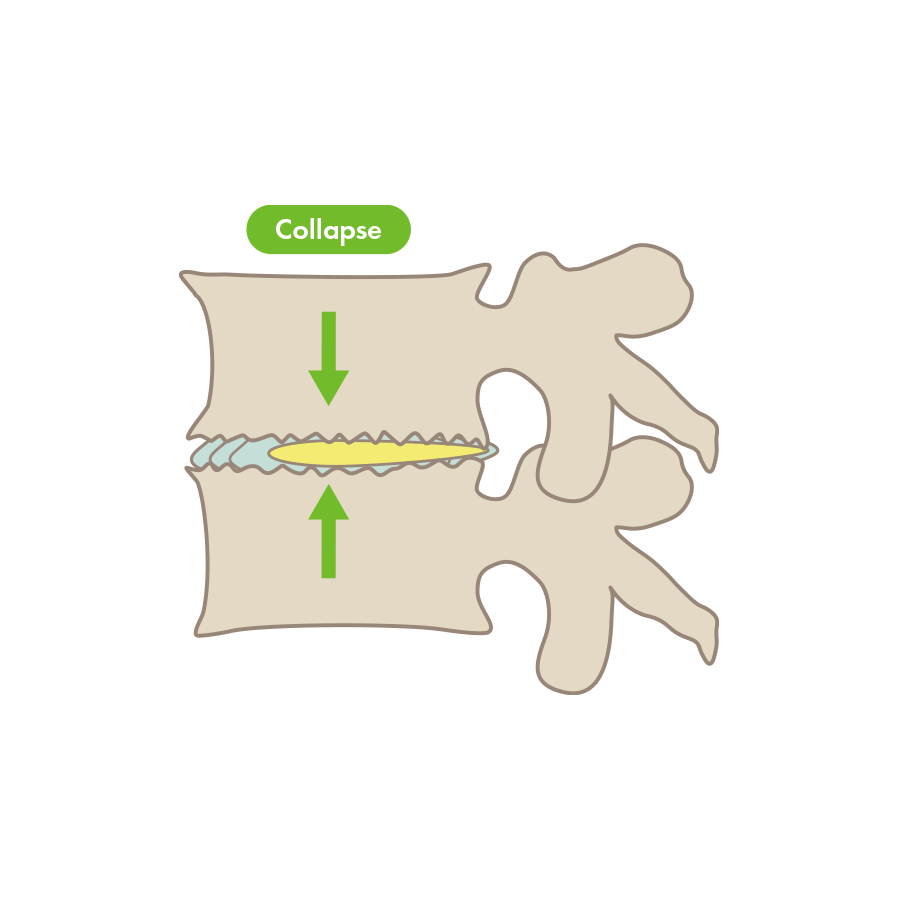
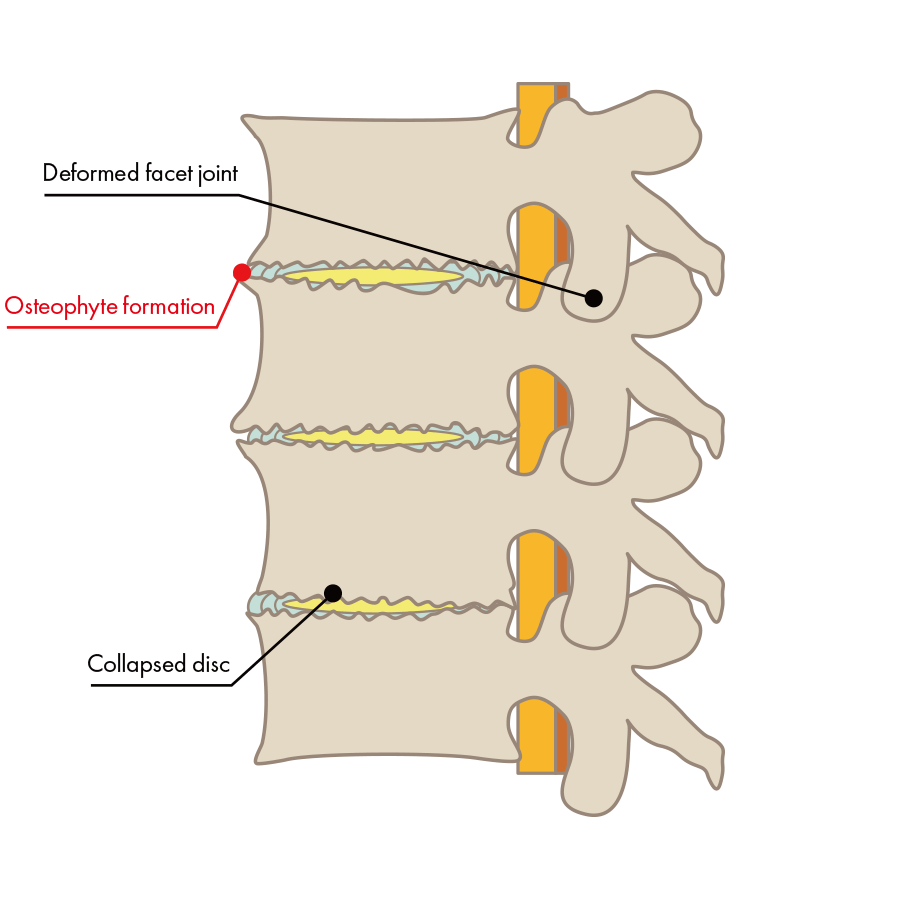
The main cause is deterioration of the intervertebral discs brought on by genetic factors and the burdens of aging and everyday life. The nucleus pulposus inside the intervertebral disc is essentially full of water, but cracks in the fibrous ring that come along with the burdens of aging and everyday life cause leakage of nucleus pulposus and loss of water content, which makes the disc become thin and collapse. In particular, lifting heavy things in daily life or playing intense sports causes damage to intervertebral discs. The intervertebral disc will appear dark on an X-ray or MRI, and its collapsed condition can be confirmed.
What is the cause of pain from herniated discs?
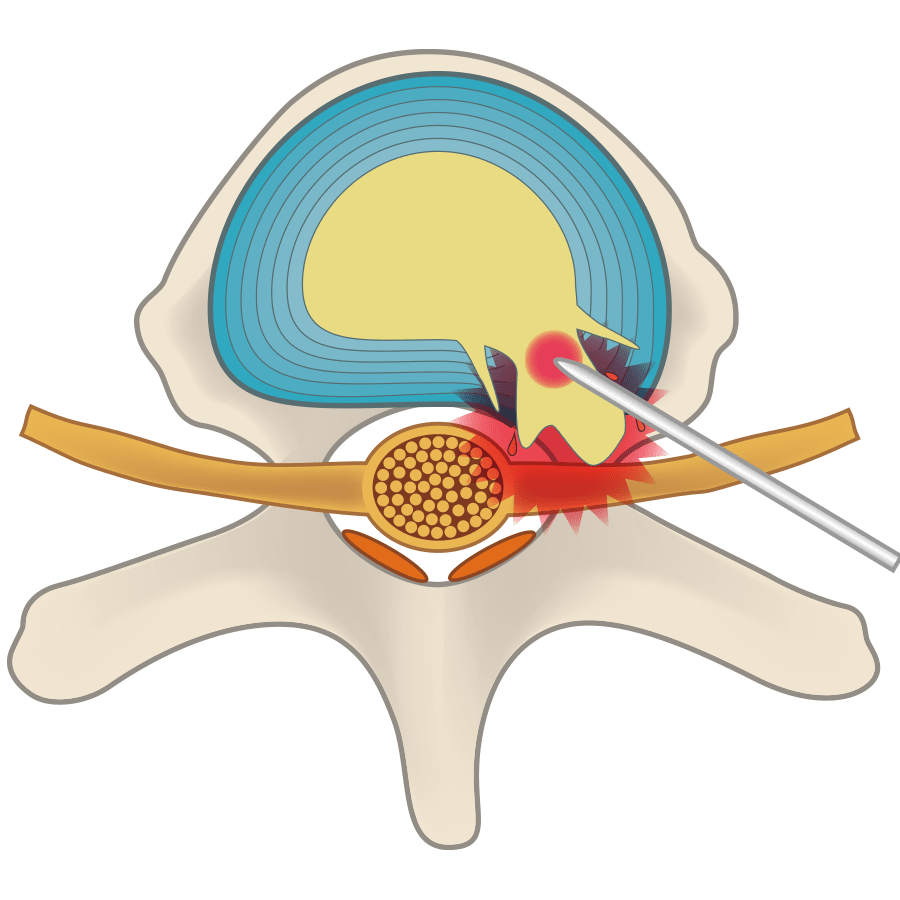
It was previously considered a mystery if there was no pain even when a disc was severely herniated or, vice versa, when serious pain came from a mildly herniated disc, but recently we’ve come to understand that, as a result of protruding nucleus pulposus causing inflammation, that inflammation spreads to nearby nerves and leads to the appearance of pain. Also, it has been established that the inflammation from protruding nucleus pulposus may disappear naturally within a fixed period (a few months). Metaphorically speaking, like an open fire, if it is given new fuel, it will burn furiously, but if some time passes, it will be the same as a fire that burns out. And cinders will remain after the fuel has burned up. With herniation, if it is naturally assimilated after the inflammation, it may remain like those cinders. The cinders-like remaining herniation can look severe in an image examination, but there are no symptoms because it is post-inflammation.
The pain from a herniated disc is not physical pressure on the nerves from escaped nucleus pulposus, the cause is inflammation due to fresh nucleus pulposus escaping.
This means, in other words, that people whose pain has continued for several months constantly have new nucleus pulposus continuing to leak out. On the other hand, it means that people whose pain has improved are experiencing a situation in which leakage of nucleus pulposus has stopped. This is extremely important. Surgery removes leaked nucleus pulposus and makes inflammation go away, but since it cannot close cracks in the fibrous ring, nucleus pulposus will continue to leak, which is the reason for the high recurrence rate (around 30%).
Surgical operation
Love's Discectomy
This is a surgical procedure that has been performed for a long time to deal with disc herniation. It is designed to relieve pressure on the nerve by surgically removing the protruding part of the discs that is causing it. The operation is completed through a wide incision on the back under general anesthesia for about 30 minutes to an hour. Patients are required to stay in bed for one more day after the procedure. Hospitalization usually lasts for about a month. Because the incision is wide, the burden on the body is quite heavy with high risk of infection and nerve damage. Rehabilitation and regular hospital visits are also required for a while.
Advantages of Love's Method
Since the surgery is performed under direct visual observation, there is less chance of missing a lesion. In addition, it is easy to feel the post-operative improvement at an early stage because the hernia that is pressing the nerve is removed.
Disadvantages of Love's Method
Patients need to be hospitalized for about a month. Because the incision is wide, the burden on the body is quite heavy with high risk of infection and nerve damage. There is also a possibility that the hernia will recur after treatment.
Minimally Invasive Discectomy
These less invasive surgical methods use endoscope or microscope, and make it possible to shorten the operation time and the hospitalization period due to the comparatively small incisions required.
Microdiscectomy (MD)
After putting the patient under general anesthesia, an incision is done in the skin of the back and a microscope is inserted to give a magnified view while removing the herniation.
Advantages of Microdiscectomy (MD)
The incision of 3 cm is smaller than the one required for Love's Method, and there is no need to peel and separate muscles, which allows a shorter recovery period and faster discharge from the hospital.
Disadvantages of Microdiscectomy (MD)
It is less invasive than the LOVE method, but the incision is larger than the MED method, and it takes 2 to 3 weeks to be discharged from hospital.
Micro Endoscopic Discectomy (MED)
General anesthesia is performed and an endoscope allowing to have a magnified view on a monitor is inserted after the incision is made in the skin of the back. The incision is closed with a special tape, so there is no thread removal after the operation.
Advantages of Micro Endoscopic Discectomy (MED)
Patients are able to walk from the very next day after surgery, but they can be discharged from the hospital in about a week.
Disadvantages of Micro Endoscopic Discectomy (MED)
Since it is a skill-requiring operation, it can only be performed at specialized medical institutions with highly trained physicians.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD)
General anesthesia is administered and an incision is made through the skin of the back. An endoscope that gives a magnified view on a monitor is inserted. The size of the incision is even smaller than that of the MED method. A 6 mm endoscope and small 3mm forceps are used to remove the de disc hernia, and the incision is closed with a special tape, so no stiches are needed.
Advantages of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD)
A few hours after the operation the patients are able to walk, and can be discharged from the hospital on the next day. This method is less physically burdensome for patients compared to LOVE's method and requires shorter hospitalization.
Disadvantages of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD)
Since the incision is much smaller, the operation has to be performed with a narrower field of vision, which increases the risk of nerve damage. There is also a risk that the hernia will not be removed sufficiently and re-operation will be required.
Percutaneous Disc Decompression
This is a surgical procedure that does not use a scalpel, but is approached from the back using a puncture needle. Since no incision is made, the treatment can be performed as a day case.
Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD)
A puncture needle is inserted into the vertebral disc from the back under local anesthesia, and a laser fiber is passed through the needle. The nucleus pulposus (hernia part) in the intervertebral disc is irradiated with the laser and evaporating it to weaken the pressure in the intervertebral disc and make the protrusion contract towards the center of the intervertebral disc.
Advantages of Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD)
After the treatment the patient has to rest for about an hour, until the doctor checks and confirms that he can be discharged from the hospital.
This treatment is less burdensome to the body and risks of infection and complications are lower than surgical operations.
Disadvantages of Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD)
PLDD treatment is not applicable in cases of severe disc herniation.
In addition, the cost of the treatment is not covered by the Japanese health insurance, so the patient has to bear all expenses incurred.
Conservative Treatment
Medication Treatment
Medical institutions usually prescribe medicine for external use such as compresses and ointments, anti-inflammatory analgesics to suppress inflammation, and muscle relaxants to relieve back pain by relieving muscle tension when diagnosed with back pain. If the cause of low back pain is nerves, vitamins may be taken for them to recover.
Nerve Blocks
This treatment method is applied when symptoms in the lower back the lower limbs are quite severe and medication treatment dies not give sufficient effect. If acute pain or long-term pain continues, the sympathetic nerves system becomes tense and may further enhance pain, so nerve block injections are given to the nerve causing the pain or the surrounding nerves to block the transmission of pain to the brain. Nerve blocks are often chosen as a treatment method to alleviate pain and numbness, but they can not cure these symptoms as it is not a curative treatment such as surgery.
Physical Therapy
When back pain appears a rest may be taken, but longer periods of rest may prolong the symptoms. If rest is not necessary, exercises and stretching may recovery. Strengthening the abdominal muscles can help relieve strain on the lower back. Inflammation from pressure on the nerves or strain on the muscles can cause symptoms such as pain and numbness. However, training the abdominal muscles is not everything, and incorrect methods or straining the muscles may worsen back pain. Please make sure you seek the advice from a doctor.
n case conservative treatment does not help improve the pain and numbness, or if the pain is so severe that you cannot move, or if your daily life is greatly affected, surgery may be considered
Spontaneous healing of disc herniation
Not all herniated discs heal spontaneously, but in some cases, when the nucleus pulposus in the herniation that protrudes into the nerve flows out and the pressure on the nerve is relieved, the inflammation disappears and the pain goes away. However, even if the hernia disappears, it recurs, and when inflammation occurs it continues for a long time and eventually turns into chronic pain. It is recommended to consult a doctor to determine whether or not you should wait to recover naturally.
How to cure a herniated disc quickly
In conclusion, it is important to try to live a life that avoids causing these symptoms as much as possible. There is no medication, exercise, or rehabilitation that can reduce the size of disc herniation. Physical therapy, massage, and electrotherapy are not treatments that can reduce the size of disc herniation either. If you experience pain or numbness due to your posture or movement, your nerves may be irritated, so you will need to try to avoid what is causing it in your daily life.
How is our treatment effective for herniated discs?
At our clinic, we perform repair and regeneration treatment for intervertebral discs that have aged and had cracks appear in the fibrous ring. We also perform PODT, and PLDD treatment if the intervertebral disc has not aged and herniation is not protruding or extruding. However, when cracks have appeared in the intervertebral disc, it will eventually lose water content, and it is also thought that it will gradually narrow, so we recommend The Discseel® Procedure. Because The Discseel® Procedure repairs tears in the fibrous ring that are the root cause of herniated discs, it is also effective for herniation that will not improve with surgery or that has recurred after surgery. Furthermore, if the nucleus pulposus continues to leak, the intervertebral disc will collapse, and the patient’s condition will ultimately be complicated by spinal stenosis. But preventing leakage of nucleus pulposus returns the intervertebral disc’s cushion function to its resilient state and inhibits the progress of spinal stenosis.
-
The PLOT Method
(Laser And Ozone)Percutaneous Laser and Ozone Treatment

-
The PODT Method
(Ozone)Percutaneous Ozone Disc
Treatment
-
The PLDD Method
(Laser)Percutaneous Laser Disc
Decompression
Disc Herniation: FAQ
-
- Q
-
How do you diagnose whether a disc is herniated or not?
- A
-
After reviewing your current symptoms, their progression so far, and the results of your physical examination, we perform a detailed examination using MRI scans and X-rays to make a comprehensive diagnosis. An MRI is an effective way of visually confirming the presence of a hernia. An MRI examination will show the position, size, shape, and degree of nerve compression of the disc herniation, and will determine whether if it is better to leave it to heal naturally, or if treatment is necessary, which will be the most appropriate to choose. Depending on the efficiency of the MRI and the way it was taken, an MRI scan may fail to show a small hernia. Even if herniation is apparent, the numbness or pain may have a different cause. Or you may have been told that it was not a herniated disc when there was in fact a small herniation, or conversely you were mistakenly told that it was a herniated disc. It is entirely possible that you actually suffer from a different condition altogether, so please consider consulting a doctor first.
-
- Q
-
Does a quick cure for a herniated disc exist?
- A
-
All in all, it is important to try to live a life as free of symptoms as possible. Presently, there exists no medication, exercise, or rehabilitation that can reduce the size of a herniated disc. Neither can physical therapy, massages, or electrotherapy offer a cure to reduce the size of a herniated disc. If you feel pain or numbness depending on your posture or the way you move, it may be because your nerves are irritated. All in all, it is important to try to live a life as free of symptoms as possible.
-
- Q
-
How soon will I be able to walk after surgery on a herniated disc?
- A
-
Depending on the procedure, a surgical removal like PELD or MED will usually require a hospital stay of 2 or 3 days. After that, you are free to go home. The PLDD and The Discseel® Procedure, which are also performed at our hospital, are a same day treatment, so you can go home within an hour after surgery.
-
- Q
-
Is a herniated disc a dangerous condition?
- A
-
Many people can have severe symptoms that may strong enough to prevent some from sitting or walking.
-
- Q
-
What happens if a herniated disc is left untreated?
- A
-
A herniated disc is a condition in which symptoms may sometimes disappear and the disc may heal on its own. A herniated disc cannot repair or regenerate itself, but the protruding part of the disc can shrink or disappear. We try to minimize the toll of treatment by monitoring changes in symptoms before considering surgical intervention.
-
- Q
-
Will a hernia recur once removed?
- A
-
At first, the surgical removal may provide some pain relief, but the nucleus pulposus, which is in the disc, may then also leak out of the excision and cause it to recur. The Discseel® Procedure is the only method that can reduce the risk of recurrence by sealing the leaking disc.
-
- Q
-
Can I be re-operated after having already had a surgery?
- A
-
Yes, it is possible. We use a needle-based treatment, which means that you can be treated even after a previous surgical procedure. You will be examined and according to the established diagnosis, the most suitable treatment course will be determined.
-
- Q
-
If I have been diagnosed with a herniated disc, should I avoid exercising?
- A
-
Moderate exercise is necessary unless pain makes it impossible. Neglecting to exercise can cause your body muscles to weaken and make the pain more severe. Learning the right way to exercise can help alleviate your symptoms. Our clinic is working in association with a rehabilitation center specialized in back pain treatment to help you cure your back pain at root level.
-
- Q
-
What precautions should I take after a herniated disc surgery?
- A
-
After treatment for a herniated disc at our clinic, you can go home on the same day, but we ask that you wear a corset on your lower back and stay in a resting position. We also recommend that you refrain from strenuous exercise for a month or so, and that you walk and stretch moderately.
-
- Q
-
How many times will I need to go to the hospital before surgery for a herniated disc?
- A
-
In the case of treatment at our clinic, you can receive treatment on the same day after diagnosis. In some cases, you may prefer to come only for diagnosis, and choose to have treatment at a later date of your choosing.
-
- Q
-
Can I fly after my herniated disc surgery?
- A
-
Depending on your symptoms, you may be able to board a plane. In the unlikely event that you suffer from post-operative pain, your doctor may decide against io please contact our clinic if you feel anything unusual.
Targeted Conditions
-
Disc Herniation

-
Spinal Canal Stenosis

-
Sciatica

-
Spondylolisthesis

-
Disc Degeneration

-
Lumbar Spondylosis

- HOME/
- Targeted Conditions/
- Disc Herniation